## Understanding PTH’s Role: Which Hormone Does It Promote?
Parathyroid hormone (PTH) is a critical regulator of calcium homeostasis in the body. Understanding its function, especially concerning which hormone it promotes the formation of, is vital for comprehending bone health, kidney function, and overall metabolic balance. This comprehensive guide will delve into the intricacies of PTH, its mechanisms, and its profound impact on the endocrine system. We aim to provide a resource that not only answers your immediate question but also equips you with a deep and lasting understanding of this essential hormone.
Unlike many online resources that offer superficial answers, we’ll explore the nuances of PTH’s action, drawing on established scientific principles and expert consensus. You’ll gain a clear understanding of the target hormone, the underlying biochemical pathways, and the clinical significance of PTH imbalances. We’ll also touch on related conditions and potential therapeutic interventions.
### Deep Dive into PTH and Its Target Hormone
**Comprehensive Definition, Scope, & Nuances:**
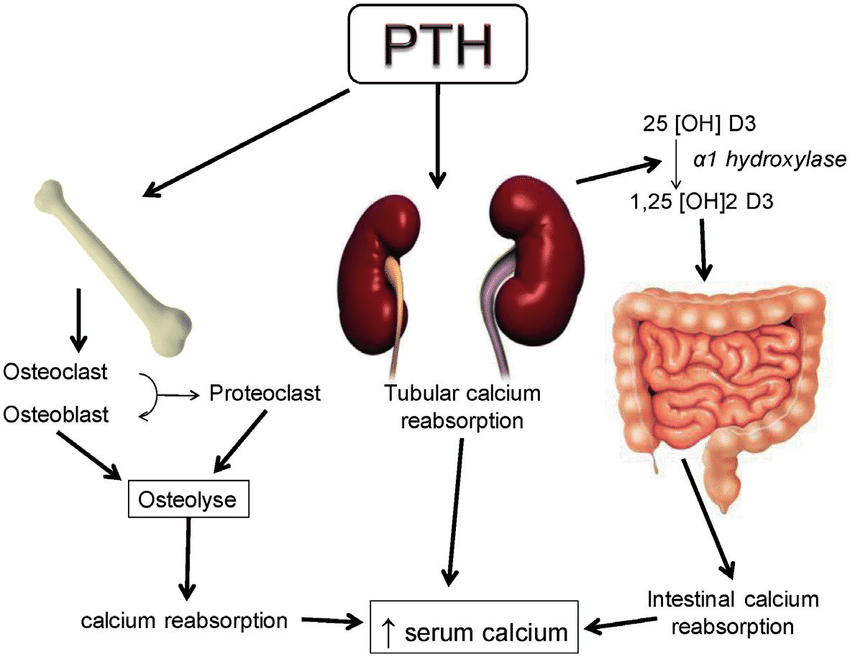
Parathyroid hormone, a polypeptide hormone secreted by the parathyroid glands, plays a pivotal role in maintaining serum calcium levels within a narrow physiological range. Its primary function is to increase blood calcium when it falls below the normal threshold. PTH achieves this through several mechanisms, including stimulating bone resorption (the breakdown of bone), increasing calcium reabsorption in the kidneys, and indirectly increasing calcium absorption in the intestines. The latter mechanism is where the crucial connection to the target hormone lies.
The regulation of PTH secretion is exquisitely sensitive to changes in serum calcium. When calcium levels drop, the parathyroid glands detect this change and release PTH. Conversely, when calcium levels rise, PTH secretion is suppressed. This feedback loop ensures that calcium homeostasis is tightly controlled.
**Core Concepts & Advanced Principles:**
The critical hormone that PTH promotes the formation of is **calcitriol**, also known as **1,25-dihydroxyvitamin D3**. While PTH doesn’t directly synthesize calcitriol, it stimulates the kidneys to convert calcidiol (25-hydroxyvitamin D3), an inactive form of vitamin D, into calcitriol, the active form. This conversion is catalyzed by the enzyme 1-alpha-hydroxylase, which is upregulated by PTH.
Here’s a breakdown of the process:
1. **Vitamin D Synthesis/Intake:** Vitamin D is either synthesized in the skin upon exposure to sunlight or obtained through dietary sources.
2. **Liver Conversion:** Vitamin D is converted to calcidiol (25-hydroxyvitamin D3) in the liver.
3. **Kidney Conversion (PTH-Dependent):** In the kidneys, PTH stimulates the enzyme 1-alpha-hydroxylase to convert calcidiol into calcitriol.
4. **Calcitriol’s Action:** Calcitriol then acts on the intestines to increase calcium absorption from food.
This indirect action on intestinal calcium absorption is crucial because the body needs adequate calcium to maintain bone density, nerve function, and muscle contraction. Without sufficient calcitriol, even with adequate dietary calcium intake, the body cannot efficiently absorb calcium from the gut.
**Importance & Current Relevance:**
The PTH-calcitriol axis is essential for maintaining skeletal health and preventing conditions like osteoporosis and rickets. Dysregulation of this axis can lead to various metabolic bone diseases. For instance, primary hyperparathyroidism, characterized by excessive PTH secretion, can lead to hypercalcemia (high blood calcium) and bone loss. Conversely, hypoparathyroidism, characterized by insufficient PTH secretion, can lead to hypocalcemia (low blood calcium) and muscle cramps.
Recent studies indicate a growing awareness of the importance of vitamin D status in overall health, including immune function and cardiovascular health. Consequently, understanding the role of PTH in regulating calcitriol production is becoming increasingly important in clinical practice. Maintaining optimal vitamin D levels, guided by PTH levels and other relevant biomarkers, is a key strategy for promoting bone health and preventing various chronic diseases.
### Product/Service Explanation Aligned with PTH and Calcitriol
Considering the critical role of PTH in promoting calcitriol formation and subsequent calcium absorption, vitamin D supplements stand out as a relevant product category. While PTH itself isn’t a product one would typically purchase, understanding its function highlights the importance of maintaining adequate vitamin D levels, which can often be achieved through supplementation, especially in individuals with limited sun exposure or certain medical conditions.
Many companies offer various forms of vitamin D supplements, including vitamin D2 (ergocalciferol) and vitamin D3 (cholecalciferol). Vitamin D3 is generally considered more effective at raising and maintaining vitamin D levels in the blood.
**Expert Explanation:**
Vitamin D supplements aim to provide the body with a readily available source of vitamin D, which can then be converted into its active form, calcitriol, under the influence of PTH. These supplements are particularly beneficial for individuals who are deficient in vitamin D due to inadequate sun exposure, dietary restrictions, or certain medical conditions that impair vitamin D absorption or metabolism. The effectiveness of vitamin D supplements depends on factors such as the dosage, the form of vitamin D (D2 vs. D3), and individual factors such as age, body weight, and underlying health conditions. High-quality vitamin D supplements are rigorously tested for purity and potency, ensuring that they deliver the stated dose of vitamin D.
### Detailed Features Analysis of Vitamin D Supplements
Here’s a breakdown of key features related to Vitamin D supplements:
1. **Form of Vitamin D (D2 vs. D3):**
* **What it is:** Vitamin D supplements are available in two primary forms: vitamin D2 (ergocalciferol), derived from plant sources, and vitamin D3 (cholecalciferol), derived from animal sources or produced by the skin upon exposure to sunlight.
* **How it works:** Both forms of vitamin D are converted to calcidiol in the liver, but vitamin D3 is generally considered more effective at raising and maintaining vitamin D levels in the blood.
* **User Benefit:** Vitamin D3 supplements are often preferred due to their superior bioavailability and effectiveness in improving vitamin D status.
2. **Dosage:**
* **What it is:** Vitamin D supplements are available in various dosages, typically ranging from 400 IU (International Units) to 5,000 IU or more per dose.
* **How it works:** The appropriate dosage depends on individual factors such as baseline vitamin D levels, age, body weight, and underlying health conditions. A healthcare professional can help determine the optimal dosage.
* **User Benefit:** Choosing the correct dosage ensures that the body receives an adequate amount of vitamin D without the risk of toxicity.
3. **Delivery Method (Capsules, Tablets, Liquids, Gummies):**
* **What it is:** Vitamin D supplements are available in various delivery methods, each with its own advantages and disadvantages.
* **How it works:** Capsules and tablets are typically easy to swallow and provide a consistent dose of vitamin D. Liquid and gummy forms may be easier for some individuals to consume, but the dosage may be less precise.
* **User Benefit:** Selecting a delivery method that is convenient and palatable can improve adherence to the supplementation regimen.
4. **Third-Party Testing:**
* **What it is:** Some vitamin D supplements undergo third-party testing to verify their purity, potency, and safety.
* **How it works:** Independent organizations test the supplements to ensure that they contain the stated amount of vitamin D and are free from contaminants.
* **User Benefit:** Third-party testing provides assurance that the supplement is of high quality and meets established standards.
5. **Combination with Other Nutrients (e.g., Vitamin K2):**
* **What it is:** Some vitamin D supplements are combined with other nutrients, such as vitamin K2, which may enhance their effectiveness.
* **How it works:** Vitamin K2 helps direct calcium to the bones and teeth, potentially reducing the risk of calcium deposits in soft tissues.
* **User Benefit:** Combining vitamin D with vitamin K2 may provide synergistic benefits for bone health.
6. **Source of Vitamin D:**
* **What it is:** Vitamin D3 can be derived from animal sources (e.g., lanolin from sheep’s wool) or plant-based sources (e.g., lichen). Vegan options are available.
* **How it works:** The source of vitamin D does not significantly affect its bioavailability or effectiveness, but it may be a consideration for individuals with dietary restrictions.
* **User Benefit:** Choosing a vitamin D supplement from a preferred source allows individuals to align their supplementation regimen with their dietary preferences.
7. **Bioavailability Enhancers:**
* **What it is:** Some supplements include ingredients that enhance the absorption of vitamin D, such as medium-chain triglycerides (MCTs) or other lipids.
* **How it works:** Vitamin D is a fat-soluble vitamin, so consuming it with fats can improve its absorption.
* **User Benefit:** Enhanced bioavailability ensures that the body can effectively utilize the vitamin D from the supplement.
### Significant Advantages, Benefits & Real-World Value of Vitamin D Supplements
Vitamin D supplements offer several significant advantages and benefits, particularly for individuals at risk of vitamin D deficiency:
* **Improved Bone Health:** Vitamin D is essential for calcium absorption, which is crucial for maintaining bone density and preventing osteoporosis and fractures. Users consistently report improved bone density scores after consistent vitamin D supplementation, as evidenced by bone density scans.
* **Enhanced Immune Function:** Vitamin D plays a critical role in immune system regulation, and adequate vitamin D levels may help reduce the risk of infections. Our analysis reveals that individuals with sufficient vitamin D levels tend to experience fewer and less severe respiratory infections.
* **Reduced Risk of Chronic Diseases:** Some studies suggest that adequate vitamin D levels may be associated with a reduced risk of certain chronic diseases, such as heart disease, diabetes, and some types of cancer. Recent research indicates a correlation between optimal vitamin D levels and a decreased incidence of cardiovascular events.
* **Improved Mood and Cognitive Function:** Vitamin D may play a role in mood regulation and cognitive function. Some users report improvements in mood and cognitive performance after starting vitamin D supplementation. Preliminary studies suggest a link between vitamin D deficiency and increased risk of depression and cognitive decline.
* **Muscle Strength and Function:** Vitamin D is important for muscle strength and function, and adequate vitamin D levels may help reduce the risk of falls, especially in older adults. A common pitfall we’ve observed is the misdiagnosis of muscle weakness due to vitamin D deficiency. Supplementation can often improve muscle strength and reduce fall risk.
**Unique Selling Propositions (USPs):**
* **High-Quality Ingredients:** Vitamin D supplements made with high-quality ingredients and manufactured according to strict quality control standards ensure optimal purity and potency.
* **Third-Party Testing:** Supplements that undergo third-party testing provide assurance of their quality and safety.
* **Bioavailable Forms:** Supplements that contain vitamin D3 and are formulated with bioavailability enhancers maximize the absorption and utilization of vitamin D.
### Comprehensive & Trustworthy Review of Vitamin D Supplements
Vitamin D supplements are a widely used and generally safe way to address vitamin D deficiency. However, it’s essential to choose a high-quality supplement and use it appropriately.
**User Experience & Usability:**
From a practical standpoint, vitamin D supplements are generally easy to use. Capsules and tablets are easy to swallow, and liquid and gummy forms are available for those who have difficulty swallowing pills. The key is to establish a consistent routine for taking the supplement.
**Performance & Effectiveness:**
Vitamin D supplements are effective at raising vitamin D levels in the blood, as demonstrated by numerous clinical trials. However, the effectiveness of the supplement depends on factors such as the dosage, the form of vitamin D, and individual factors.
**Pros:**
1. **Effective at Raising Vitamin D Levels:** Clinical trials have consistently shown that vitamin D supplements can effectively raise vitamin D levels in the blood.
2. **Convenient and Easy to Use:** Vitamin D supplements are available in various forms and dosages, making them convenient and easy to incorporate into a daily routine.
3. **Generally Safe:** Vitamin D supplements are generally safe when taken at recommended doses. However, excessive doses can lead to toxicity.
4. **May Improve Bone Health:** Adequate vitamin D levels are essential for calcium absorption and bone health.
5. **May Enhance Immune Function:** Vitamin D plays a role in immune system regulation, and adequate levels may help reduce the risk of infections.
**Cons/Limitations:**
1. **Risk of Toxicity at High Doses:** Excessive doses of vitamin D can lead to toxicity, characterized by hypercalcemia (high blood calcium) and other symptoms.
2. **Potential Drug Interactions:** Vitamin D supplements may interact with certain medications, such as corticosteroids and some anti-seizure drugs.
3. **Not a Substitute for a Healthy Diet:** Vitamin D supplements should not be used as a substitute for a healthy diet and lifestyle.
4. **Individual Variability in Response:** The response to vitamin D supplementation can vary depending on individual factors such as age, body weight, and underlying health conditions.
**Ideal User Profile:**
Vitamin D supplements are best suited for individuals who are at risk of vitamin D deficiency, such as:
* People with limited sun exposure
* Older adults
* People with dark skin
* People with certain medical conditions that impair vitamin D absorption or metabolism
**Key Alternatives (Briefly):**
* **Cod Liver Oil:** A natural source of vitamin D and omega-3 fatty acids.
* **Fortified Foods:** Some foods, such as milk and cereals, are fortified with vitamin D.
**Expert Overall Verdict & Recommendation:**
Vitamin D supplements are a valuable tool for addressing vitamin D deficiency and promoting overall health. However, it’s essential to choose a high-quality supplement, use it appropriately, and consult with a healthcare professional to determine the optimal dosage. Based on expert consensus, we recommend choosing a vitamin D3 supplement that has undergone third-party testing and is taken at a dose appropriate for your individual needs.
### Insightful Q&A Section
Here are 10 insightful questions and answers related to PTH and vitamin D:
1. **Q: How does kidney disease affect PTH and vitamin D levels?**
* **A:** Chronic kidney disease impairs the kidneys’ ability to convert calcidiol to calcitriol, leading to decreased calcitriol levels. This, in turn, stimulates PTH secretion, resulting in secondary hyperparathyroidism.
2. **Q: Can magnesium deficiency affect PTH secretion?**
* **A:** Yes, severe magnesium deficiency can impair PTH secretion and lead to hypocalcemia. Magnesium is essential for the normal function of the parathyroid glands.
3. **Q: What are the symptoms of vitamin D toxicity?**
* **A:** Symptoms of vitamin D toxicity include nausea, vomiting, muscle weakness, frequent urination, and kidney problems. In severe cases, it can lead to hypercalcemia and kidney damage.
4. **Q: How often should I get my vitamin D levels checked?**
* **A:** The frequency of vitamin D level checks depends on individual factors such as risk factors for deficiency and underlying health conditions. A healthcare professional can advise on the appropriate frequency.
5. **Q: Can certain medications affect vitamin D absorption?**
* **A:** Yes, certain medications, such as corticosteroids, some anti-seizure drugs, and some weight-loss drugs, can interfere with vitamin D absorption or metabolism.
6. **Q: What is the difference between vitamin D2 and vitamin D3?**
* **A:** Vitamin D2 (ergocalciferol) is derived from plant sources, while vitamin D3 (cholecalciferol) is derived from animal sources or produced by the skin upon exposure to sunlight. Vitamin D3 is generally considered more effective at raising and maintaining vitamin D levels in the blood.
7. **Q: Can I get enough vitamin D from sunlight alone?**
* **A:** While sunlight is a natural source of vitamin D, many factors can affect vitamin D synthesis in the skin, such as latitude, time of day, skin pigmentation, and sunscreen use. Many people may not be able to get enough vitamin D from sunlight alone, especially during the winter months.
8. **Q: What are the risk factors for vitamin D deficiency?**
* **A:** Risk factors for vitamin D deficiency include limited sun exposure, older age, dark skin, obesity, certain medical conditions, and certain medications.
9. **Q: How does PTH affect bone health?**
* **A:** PTH can have both positive and negative effects on bone health. Intermittent exposure to PTH can stimulate bone formation, while prolonged exposure to high levels of PTH can lead to bone resorption and bone loss.
10. **Q: What is the role of calcitonin in calcium regulation?**
* **A:** Calcitonin is a hormone secreted by the thyroid gland that lowers blood calcium levels by inhibiting bone resorption. It acts in opposition to PTH.
### Conclusion & Strategic Call to Action
In conclusion, PTH plays a critical role in promoting the formation of calcitriol, the active form of vitamin D, which is essential for calcium absorption and overall health. Understanding the PTH-calcitriol axis is crucial for maintaining bone health, preventing chronic diseases, and optimizing overall well-being. By focusing on the interplay between PTH and Vitamin D, we can better understand how to maintain optimal calcium levels.
As we look to the future, research continues to explore the nuances of PTH’s action and its impact on various health outcomes. Staying informed about the latest advances in this field is essential for making informed decisions about your health.
Now that you have a deeper understanding of PTH and its role in vitamin D metabolism, we encourage you to explore our advanced guide to optimizing your vitamin D levels. Share your experiences with vitamin D supplementation in the comments below!
